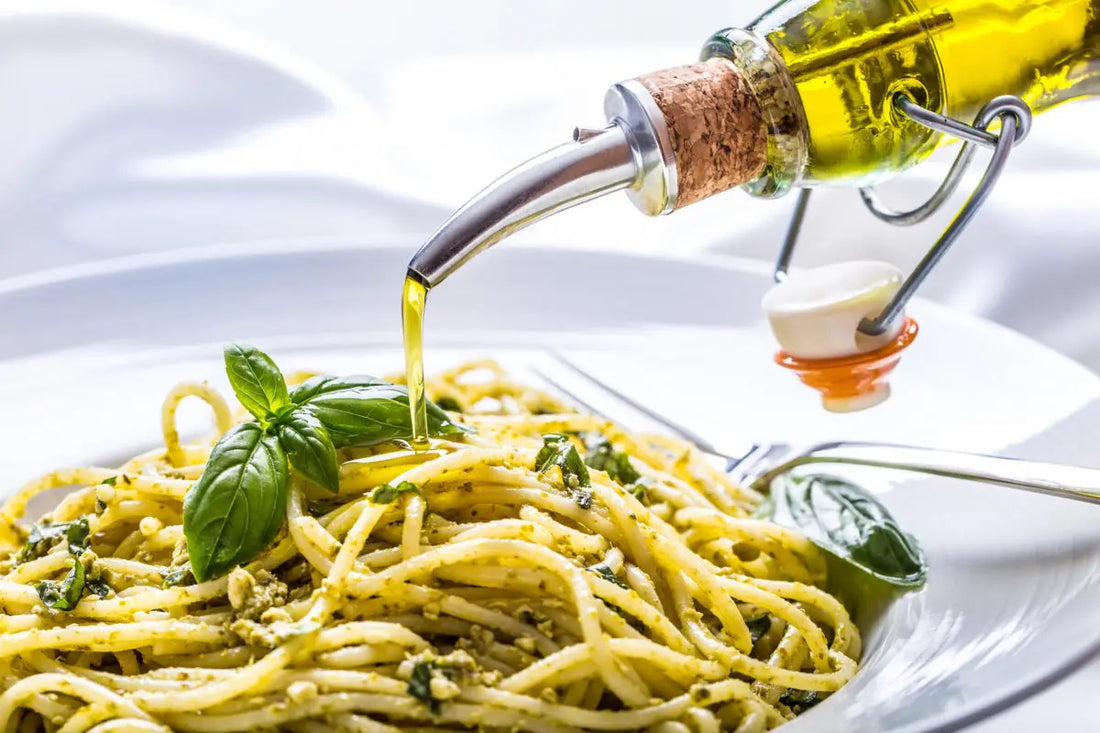
Olive oil has always been seen as a “healthy” staple in the kitchen, with the cultivation of olives dating back to around 5000 B.C. on Crete and the Greek Islands. But there are also those who believe it started in Jordan, Persia, or even the Valleys of the Nile. And then you might also hear it originating in Israel where stone presses dating back 7,000 years ago were found.
Wherever it originated from, we know that major civilizations of the Mediterranean have played an important part in disseminating olive oil throughout time, and is still a huge part of Mediterranean cuisine. Currently, the countries who consume the most olive oil are Italy, Greece, Spain, and Morocco, with North America and northern Europe catching up.
Olive Oil Nutrition Facts
Olive oil is of course, made from olives, the fruit of the olive tree. In one tablespoon of olive oil, there are 119 calories and no cholesterol, sodium, carbohydrates, protein, or fiber. Here are the nutrition facts for one serving of olive oil (1 tablespoon):
- Total Fat: 14 g
- Saturated Fat: 2 g
- Monounsaturated Fat: 10 g
- Polyunsaturated Fat: 1.4 g
- Total Omega-3 fatty acids: 103 mg
- Total Omega-6 fatty acids: 1.3 g
- Vitamin E: 1.9 mg
- Vitamin K: 8.1 mcg
Olive oil is 100 percent fat, but as we know, there are good fats (like the ones you find in fish) and bad fats (the ones you find in processed foods). The exact fatty acid composition of olive oil depends on the type of olive oil tree, the time of harvest, and the processing method, so try not to get too caught up in that aspect.
Other than the two important fat-soluble nutrients vitamins E and K, and the healthy fats that olive oil possesses, it also has polyphenols – antioxidants that have been shown to help with illnesses like depression, obesity, diabetes, cancer, and more. You can find polyphenols in these foods:
- Red cabbage
- Berries
- Red and purple grapes
- Radishes
- Tea
- Apples
- Broccoli
Benefits of Olive Oil
Olive oil contains at least 30 different phenolic compounds and has the ability to reduce oxidative stress in the body, which is what helps reduce the risk of many diseases and illnesses. Here are some of the benefits of olive oil.
Improves heart health
One study showed that 11 young men found improved lipids when they incorporated olive oil into their diet while keeping their calorie intake the same. A group of 28 people over the age of 50 also found similar results.
When your immune system begins to fight your own body as a result of a poor diet, stress, or other factors, inflammatory responses are triggered and could lead to dangerous disease-causing inflammation. Studies have shown that the protective effects of a Mediterranean diet rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) helps decrease the risk of cardiac death by 30 percent and sudden cardiac death by 45 percent.
Helps fight cancer
Researchers have found that olives and olive oil contain a great amount of antioxidants, containing acteosides, hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and phenyl propionic acids. They also have other compounds that are deemed to be anticancer agents (squalene and terpenoids) as well as the peroxidation-resistant lipid oleic acid.
Can help prevent or treat diabetes
Fatty acids like the ones found in olive oil, influence glucose metabolism by altering cell membrane function, enzyme activity, insulin signaling, and gene expression. Consuming polyunsaturated and/or monounsaturated fats have been found to have beneficial effects on insulin sensitivity and is likely to reduce the risk of type-2 diabetes.

Good for skin health
Diets high in these healthy fats can also help counter the harmful effects your skin goes through from UV light, free radicals, poor diets, food allergies, and exposure to toxicity.
Having a good source of antioxidants and vitamins E and K, olive oil can also help hydrate your skin, speed up wound healing, and help fight infections or hormonal imbalances that can lead to acne, eczema, and other skin conditions.
Helps fight depression
These healthy fats we keep talking about have hormone-balancing, anti-inflammatory effects that can prevent neurotransmitter dysfunction. Mood or cognitive disorders can happen when the brain doesn’t get enough “happy hormones” like serotonin or dopamine. These are necessary for regulating mood, getting good sleep, and processing thoughts.
Diets low in fat are often seen linked to higher rates of depression and anxiety, and one study found that monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat intake had an inverse relationship with risk of depression, while trans fat intake and risk of depression had a linear relationship. This shows that consuming healthy fats could help fight depression and mood disorders.
Other benefits that have been noted are:
- Osteoporosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Alzheimer’s
- Gut flora function
- Obesity

Why is Olive Oil Paleo?
If you’re on a paleo diet, then you’re in luck, because olive oil is a paleo food. Why, you ask? Simply because olives are an ancient food that our ancestors were able to gather back in the day. The rule of thumb is if a caveman didn’t eat it, neither should you. Learn more about paleo diets here.
And here are some other paleo fats you could consider.
- Coconut oil
- Palm oil
- Ghee
- Lard
- Tallow
How to Choose and Store Olive Oil?
A lot of people don’t know that the shelves at their grocery stores are full of “fake” olive oil – diluted with GMO canola oil, enhancers, other oils, and even water.
Brands will try to trick you into thinking whatever is in their bottle is extra special by using words like “first pressed”, “cold pressed”, or “imported from Italy.” That’s why it’s good to do your research to buy olive oils from trusted brands that meet some criteria.
There are several grades of olive oil that represents its quality.
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) – contains the highest concentration of polyphenols and has the best flavor. It’s the first pressing of the olives, doesn’t use solvents, and can only contain up to 0.8 percent acidity.
Virgin olive oil – also from the first pressing, but contains up to 2 percent acidity, and the flavor is not as good as EVOO.
Refined olive oil – has undergone processing that may include heat, solvents, and/or filtration to improve the flavor and aroma of poor quality oil.
Regular olive oil – can also be called light or mild olive oil – all are blends of refined and virgin olive oil that have gone through fine filtration to remove most of the natural color, aroma, and flavor.
Here are some things to think about when buying olive oil.
- Dark bottles are best
- An “extra virgin” distinction is important
- Look out for precise point of production and certifications
- Beware of words like “cold pressed” and “first pressed”
- Try to find the harvest or best-by date
- Don’t worry about color because different types of olives yield different colored oils
- Look for the USDA organic seal
Let us know what you could benefit from olive oil!

 Log in
Log in
