Camel milk is lower in lactose than cow milk, but has a higher amount of zinc, which helps fight free-radical damage, infertility, diabetes, promotes liver health, and so much more. This makes camel milk an easy way to help people who are prone to infection, have a major sweet tooth, or are exposed to foods and environments that cause the body to produce free radicals.
Zinc is a type of metal you might have heard as an effective cold remedy, meaning you probably only need it every once in a while when you get sick.
However, zinc is needed in small amounts every day in order for your body to perform important functions each day. Hormone production, growth and repairment, improving immunity, and facilitating digestion are just a few things.
This element is actually in all bodily tissue and is needed for healthy cell division, acting as an antioxidant within the body, fighting free-radical damage, and slowing the aging process.
Zinc deficiency is common all around the world, including the US. It occurs when someone doesn’t eat enough foods that contain it or has problems absorbing it due to digestive disorders. So it’s good to know the benefits of zinc, how much you need, how to obtain it, and the symptoms of zinc deficiency.
Benefits of Zinc
Skin care: Zinc has been shown to be an effective home remedy for curing pimples and acne as it regulates and controls the amount of testosterone in the body. It is also involved in collagen synthesis, which helps with normalizing the amount of skin oils and helps maintain healthy skin. Even with open cuts or sores that lead to infection, it helps by stimulating the white blood cell count.
Eczema: Also called “atopic dermatitis”, eczema is an inflammatory and chronic disorder of the skin, and it is mainly caused by a deficiency of zinc in the body. It plays an important role in healing chronic infections and assists the body in restoring its ability to heal properly and completely.
Prostate disorder: Zinc is very important in dealing with prostate disorders. Not having enough zinc causes enlargement of the prostate gland and makes it vulnerable to cancer. It’s recommended to take 15mg of zinc every day, under close medical observation, when suffering from a prostate disorder, but of course, consulting your doctor is always the best way to go.
Cognitive function: Recent research has shown zinc to have a strong impact on mental function because it can pair up with vitamin B6 to ensure the proper function of neurotransmitters that communicate with the body. For those who have suffered from an injury, extra zinc will keep brain function strong, because the body naturally diverts it to the other parts of the body for healing purposes.

Colds and infections: Zinc supplements help in decreasing the severity and duration of colds and other mild illnesses. It reduces the amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which aggravate the body during colds or other infections. Its ability to stimulate white blood cell activity also makes it ideal for reducing colds and infections.
Other benefits include enzyme regulation, being a defense to some cancers, increasing energy levels, strengthening bones, and improving your vision.
Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
- Growth retardation
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of smell and taste senses
- Depression
- Rough or pale skin
- Weight loss
- Diarrhea
- Low blood pressure
- Hair loss
- Fatigue
- White spots under fingernails
- Poor concentration and memory
- Slowed ability to heal wounds or infections
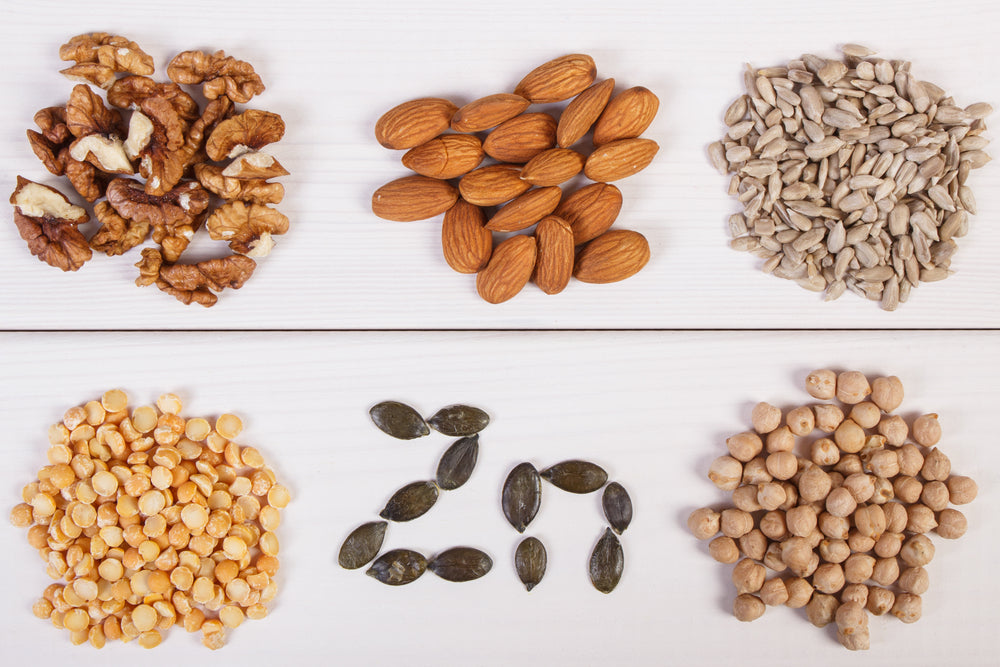
How To Get Zinc
Other than supplements in the form of syrups, gels, lozenges, and capsules, it’s important to get your zinc from food sources like:
- Meat (lamb, grass-fed beef, chicken, turkey)
- Chickpeas
- Cashews, almonds
- Pumpkin seeds
- Oysters
- Turnips
- Ginger root
- Oats
How Much Zinc Do You Need
According to the USDA, the dietary reference intakes for zinc below are based on age and gender:
Infants:
- 0–6 months: 2 milligrams/day
- 7–12 months: 3 milligrams/day
Children:
- 1–3 years: 3 milligrams/day
- 4–8 years: 5 milligrams/day
- 9 –13 years: 8 milligrams/day
Adolescents and adults:
- Males age 14 and over: 11 milligrams/day
- Females age 14 to 18 years: 9 milligrams/day
- Females age 19 and over: 8 milligrams/day
Let us know what other benefits zinc has or what you do to get enough zinc in your body!

 Log in
Log in
